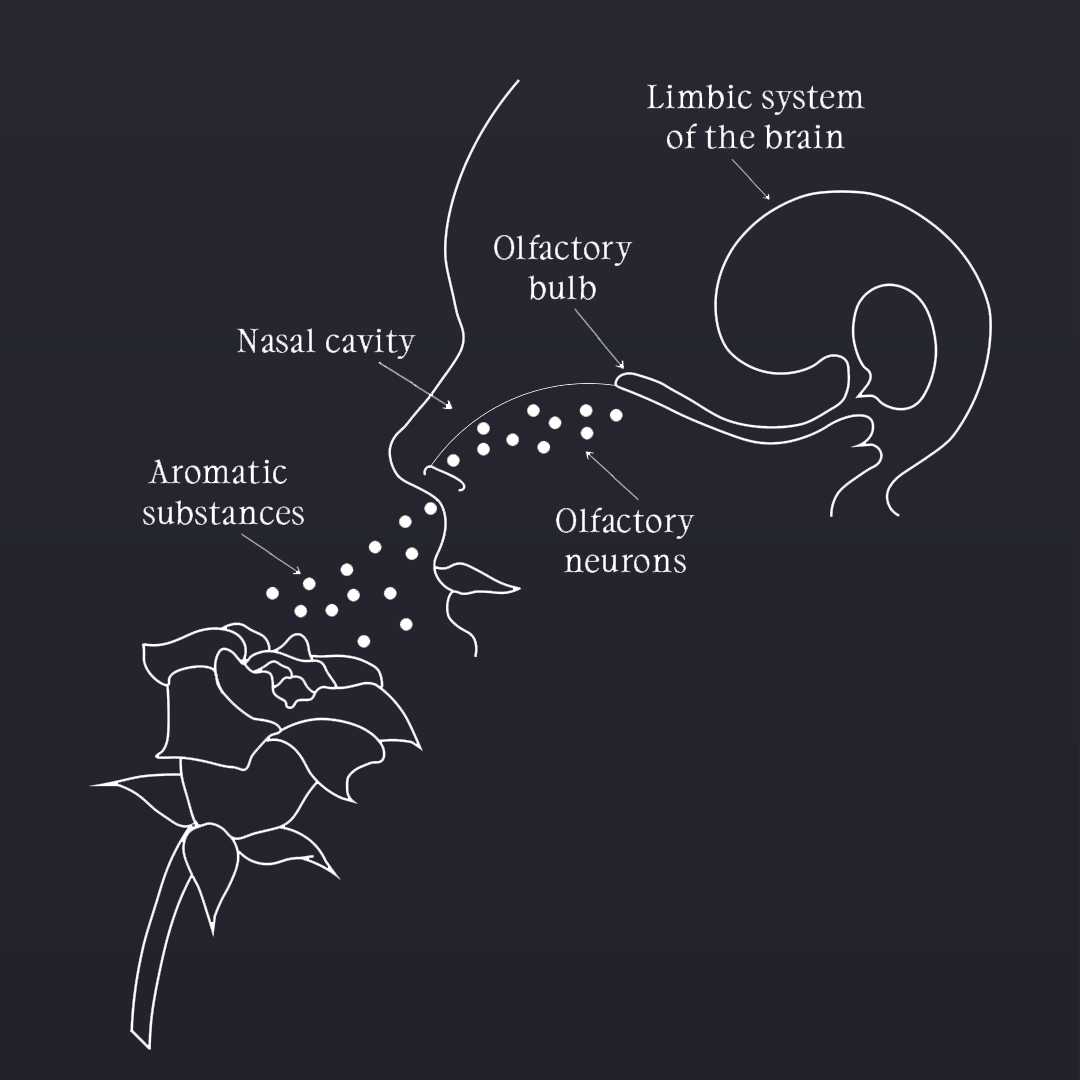
How does the aroma smell affect memory and emotions in the brain?
01. Olfactory System: When you encounter a scent, odor molecules travel through your nostrils to the olfactory epithelium, a specialized tissue in the nasal cavity. This tissue contains olfactory receptors, which are neurons that detect scent molecules.
02. Limbic System Activation: Scent information is then transmitted via the olfactory nerve to several brain structures collectively known as the limbic system. This includes the amygdala, hippocampus, and hypothalamus, among other regions.
03. Memory Formation: The hippocampus, a key structure in the limbic system, plays a crucial role in forming new memories and associating them with specific contexts, including olfactory cues. When you encounter a scent, it can trigger the recall of memories stored in the hippocampus that are associated with that particular aroma. This phenomenon is known as odor-evoked memory.
04. Emotional Response: The amygdala, another important structure in the limbic system, is heavily involved in processing emotions, particularly fear and pleasure responses. When you smell a scent, the amygdala helps evaluate its emotional significance based on past experiences and associations. Certain aromas can elicit strong emotional responses, such as joy, nostalgia, relaxation, or alertness.
05. Neurotransmitter Release: Scent molecules can influence the release of neurotransmitters in the brain, such as serotonin, dopamine, and noradrenaline, which regulate mood and emotion. For example, the scent of lavender has been shown to have calming effects, possibly due to its ability to increase serotonin levels.
06. Conditioning and Associations: Over time, repeated exposure to a scent in conjunction with certain experiences or emotions can lead to associative learning. This means that the scent becomes linked with those experiences or emotions in the brain. Subsequently encountering the scent can then evoke the associated memories and emotions.
07. Individual Variability: It’s important to note that the impact of aroma on memory and emotion can vary between individuals based on factors such as personal experiences, cultural background, and genetic predispositions.